Content
Be sure to first check with your lender if this is an option for your loan. When you make an extra payment or a payment that’s larger than the required payment, you can designate that the extra https://quickbooks-payroll.org/ funds be applied to principal. Because interest is calculated against the principal balance, paying down the principal in less time on a fixed-rate loan reduces the interest you’ll pay.
Learn accounting fundamentals and how to read financial statements with CFI’s free online accounting classes. Common amortizing loans include auto loans, home loans, and personal loans. Depreciable property is an asset that is eligible for depreciation treatment in accordance with IRS rules. Accumulated depreciation is the cumulative depreciation of an asset up to a single point in its life.
Amortization of intangible assets
When the competition gets serious, the edge goes to those who know how and why real business strategy works. Essentials for mastering the case-building process and delivering results that win approval, funding, and top-level support. The complete, amortization concise guide to winning business case results in the shortest possible time. For twenty years, the proven standard in business, government, education, health care, non-profits. For more on the nature of expenses of various kinds, see Expense.
Amortization appears on the Income Statement as an expense, like depreciation expense, usually under Operating Expenses, or «Selling, General and Administrative Expenses. For coverage of the similar accounting practice, depreciation, see the article Depreciation Expense. Typically, more money is applied to interest at the start of the schedule.
Understanding Discriminatory Restrictive Covenants
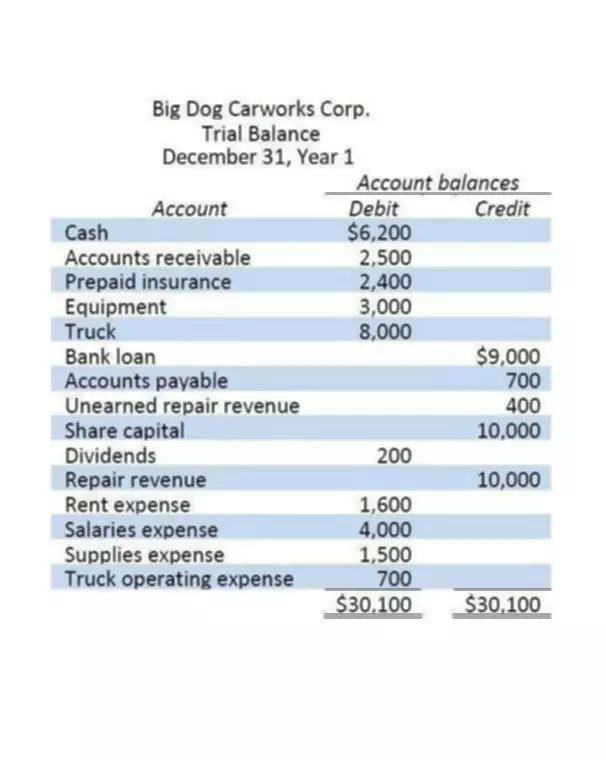
As the outstanding loan balance decreases over time, less interest will be charged, so the value of this column should increase over time. Amortization can refer to the process of paying off debt over time in regular installments of interest and principal sufficient to repay the loan in full by its maturity date. A higher percentage of the flat monthly payment goes toward interest early in the loan, but with each subsequent payment, a greater percentage of it goes toward the loan’s principal.
Were loosened in the 1990s and 2000s, the IRS often insisted that assets could only be amortized if they had a real, finite lifespan and actually lost value over time. Amortization, in finance, the systematic repayment of a debt; in accounting, the systematic writing off of some account over a period of years. Looking down through the schedule, you’ll see payments that are further out in the future. As you read through the entries, you’ll notice that the amount going to interest decreases and the amount going toward the principal increases. The best way to understand amortization is by reviewing an amortization table. If you have a mortgage, the table was included with your loan documents. Cierra Murry is an expert in banking, credit cards, investing, loans, mortgages, and real estate.
Comentarios recientes